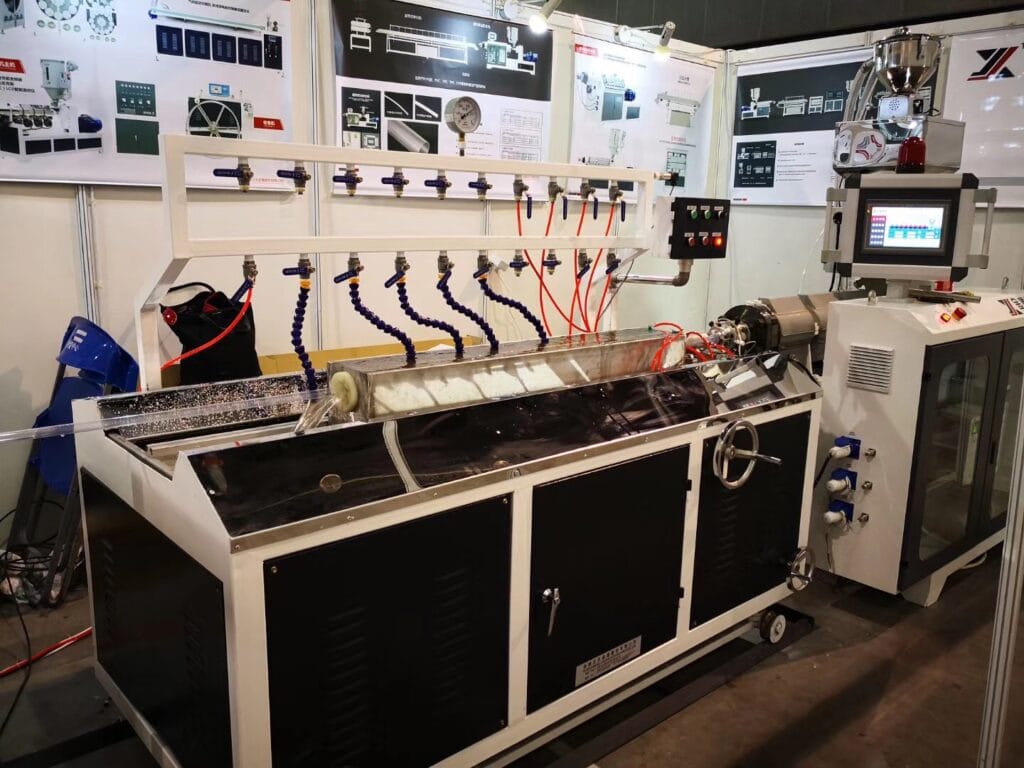
What Is an Extruder Machine? Working Principle, Types, and Key Components
If you are searching what is extruder machine, you are likely trying to understand the core equipment behind continuous manufacturing of plastics (and many other materials). In simple terms, an extruder machine takes raw material, conveys it forward, applies heat and shear to form a processable melt (or soft mass), and then forces it through a shaped die to create a continuous product.
Note: While extruders are used in food and metal industries, this guide specifically focuses on plastic extruder machines—the backbone of the modern polymer industry used to produce pipes, profiles, sheets, and films.

Now that we have defined what an extruder machine is, let’s go deeper into the working principle and the key factors that affect output stability, melt quality, and final product consistency.
The Core Process: How Does an Extruder Machine Work?
Feeling that simple explanations of this extrusion equipment leave out critical operational details? A detailed look at the extrusion process reveals the sophisticated engineering within an extruder machine.
Essentially, an extruder machine meticulously controls the transformation of solid raw material into a precisely shaped molten stream. This is achieved through a synergistic combination of conveying, heating, mixing, pressurizing, and shaping within its core components.

Working Principle: The 5 Key Stages of Extrusion
To fully appreciate the function of an extruder machine, we must look beyond a simple definition. The process is a carefully orchestrated sequence that defines the achievable product quality.
1. Precision Material Input (The Hopper and Feed Throat):
The journey begins at the hopper. Consistent and accurate feeding of the raw plastic (pellets, granules, or powder) into the extruder machine is foundational. The design of the feed throat, sometimes cooled, ensures that material flows steadily into the screw channels without premature melting or bridging.
2. The Screw – The True Heart of the Extruder:
The extruder screw is not just a simple conveyor; its complex geometry is meticulously designed. Understanding the distinct zones of a screw is critical:
- Feed Zone (Solids Conveying): Transports solid plastic particles and compacts them.
- Transition Zone (Melting): Compresses and melts the material via shear heat and barrel heaters.
- Metering Zone (Pumping): Homogenizes the melt and builds pressure for the die.

3. The Barrel – More Than Just a Container:
The barrel works in tandem with the screw. It’s not just a passive housing but a robust vessel with independently controlled heating zones to create a precise temperature gradient.
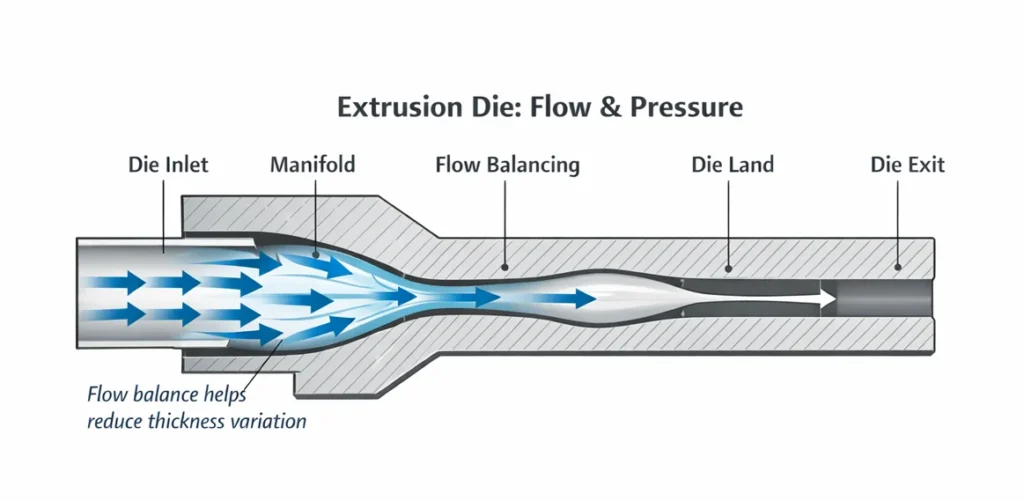
4. Pressure Development and Die Shaping:
As the molten plastic reaches the end of the screw, significant pressure is built to force the viscous melt through the die. The die’s design determines the final shape (pipe, profile, sheet).
5. Controlled Cooling and Downstream Handling:
The function of the extruder machine doesn’t end at the die exit. The extrudate must be cooled (water baths, air knives) and pulled at a constant speed to maintain dimensions.
| Internal Process Stage | Key Action of the Extruder | Critical Factors |
| Hopper & Feed Throat | Material input | Material form, drying, feed consistency |
| Screw Zones | Conveying, Melting, Pumping | Screw design (L/D ratio), compression ratio |
| Barrel Function | Thermal control | Temperature profile accuracy |
| Die & Downstream | Shaping & Solidifying | Die design, cooling rate, haul-off speed |
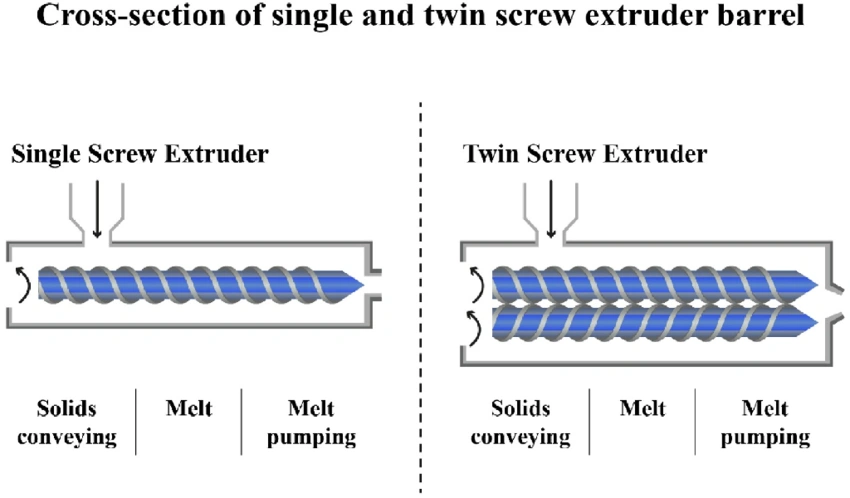
Types of Extruder Machines: Single Screw vs. Twin Screw
While single-screw extruders and twin-screw extruders cover most plastic applications, understanding their differences is key to choosing the right extruder machine.
| Type of Extrusion Equipment | Key Defining Feature(s) | Primary Application Area(s) | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Screw Plastic Extruder Machine | One rotating screw | General purpose pipes, profiles, films, sheets | Most thermoplastics (PE, PP, PVC, PS) |
| Twin-Screw Plastic Extruder Machine | Two intermeshing screws (co- or counter-rotating) | Compounding, mixing, reactive extrusion, difficult materials | PVC powder, filled plastics, blends |
| Ram Plastic Extruder Machine | Plunger pushes material billet | Materials difficult for screw extrusion | PTFE, UHMWPE |
| Multi-Screw Plastic Extruder Machine | More than two screws for intensive mixing | Specialized compounding, heat-sensitive materials | PVC, high-filler content |
| Co-Extrusion System (multiple units) | Multiple extruders feeding one multi-manifold die | Multi-layer films, pipes, profiles with distinct layers | Various, depending on layer needs |
Industry publications like Plastics Technology regularly cover advances in extrusion technology.
Critical Selection Factor: Granules or Powder?
A common scenario we see at Jinxin is clients requesting a quote for a “PVC pipe machine” without realizing that their raw material form dictates the machine type. Many assume any extruder will work, but the first question our engineers always ask is: “Are you using granules or powder?”
- Single-Screw Extruder (For Granules):
Jinxin’s single-screw extruders are designed specifically for granules (pellets). If you use pre-compounded PVC granules (or PE/PP pellets), our single-screw machines are the most efficient and cost-effective choice for your production.
- Twin-Screw Extruder (For Powder):
If you use PVC powder (dry blend), you generally need a Twin-Screw Extruder. A standard single-screw machine cannot generate the high shear required to mix and plastify powder directly. If you have powder, you must use a twin-screw machine (or pelletize your powder first).
Jinxin Tip: We ask this upfront to ensure you don’t waste time looking at the wrong equipment. If you have granules, our single-screw lines are the perfect fit.
For a detailed comparison, see Single vs. Twin-Screw Guide.
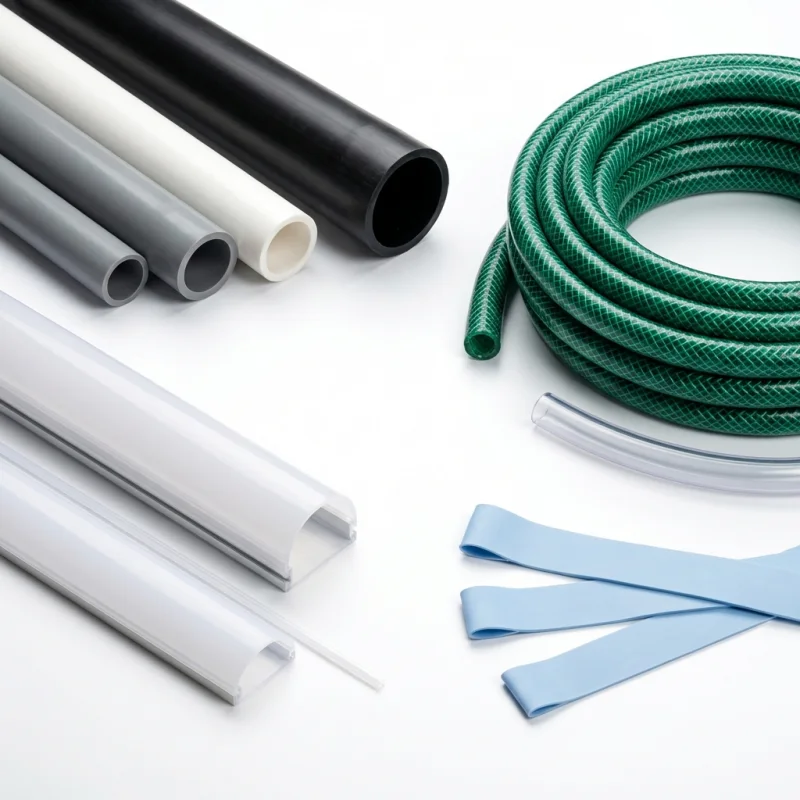
Common Applications: What Can Plastic Extruders Create?
Plastic extruder machines are incredibly versatile. Here are the most common applications:
- Pipes and Tubing: Water pipes, gas pipes, medical tubing.
- Profiles: Window frames, door seals, LED light covers.
- Sheets: Packaging, thermoforming sheets.
- Specialty: TPE elastic bands, 3D printer filaments.

Choosing the Right Extruder Machine: A Buyer’s Checklist
To ensure you buy the right extruder machine, prepare the following specifications when contacting manufacturers like Jinxin:
- Material: What plastic are you using? (e.g., HDPE granules, PVC powder, PVC granules, LDPE granules)
- Product: What is the final shape and size? (e.g., Pipe OD 110mm, Profile drawing)
- Output: How many kg/hour do you need?
- Application: Is it for a new line or upgrading an old one?
Maintenance and Operation
Routine maintenance ensures your extruder machine runs efficiently for years.
- Regular inspection of the screw and barrel for wear.
- Monitoring gearbox oil levels and temperature.
- Calibrating heater bands and thermocouples.
What Is an Extruder Machine? FAQ and Common Questions
Here are quick answers to common questions about what is an extruder machine.
Conclusion
Understanding what is an extruder machine is the first step to mastering plastic production. Whether you need a simple single-screw unit for PE pipes or a complex twin-screw system for PVC compounding, the right equipment defines your success.
At Jinxin Plastic Machinery, we specialize in high-performance plastic extruder machines tailored to your production goals.
Ready to start? Contact Jinxin today with your product specs, and let us help you build the perfect extrusion line.
Explore Topics
Filter by Specs
Have Technical Questions?
Our engineering team is ready to help with your extrusion process or machine configuration.

Jason Shen
Jason is the founder of Jinxin Extruder and a veteran engineer with over 20 years of hands-on experience in plastic machinery.
Starting his career on the shop floor, he mastered every technical detail—from electrical wiring to complex troubleshooting.
Today, he personally oversees final inspections, ensuring every machine is built with deep technical expertise and field-tested reliability.