O mundo do processamento de elastómeros termoplásticos apresenta desafios únicos para os fabricantes. Desde a seleção do material à configuração do equipamento, a obtenção de uma qualidade consistente na extrusão de TPE requer conhecimentos e equipamento especializados. No entanto, com uma compreensão adequada e a maquinaria correta, estes desafios transformam-se em oportunidades para a inovação de produtos e o crescimento do negócio.
O que é o material TPE?
O TPE (Elastómero Termoplástico) é uma classe de polímeros que combina as vantagens de processamento dos termoplásticos com o desempenho funcional dos elastómeros semelhantes à borracha. Estes materiais versáteis podem ser fundidos e moldados utilizando métodos convencionais de processamento de plásticos, proporcionando flexibilidade, suavidade e resiliência semelhantes à borracha vulcanizada.
 O que é o material TPE? Desbloquear o seu potencial para o seu negócio 1
O que é o material TPE? Desbloquear o seu potencial para o seu negócio 1
Os elastómeros termoplásticos revolucionaram a indústria de processamento de plásticos ao oferecerem uma combinação única de propriedades. Como a procura de produtos TPE continua a crescer - com o o mercado mundial deverá atingir 44,46 mil milhões de dólares em 2032Compreender o que são materiais TPE e como processá-los torna-se cada vez mais valioso para os fabricantes que procuram expandir as suas ofertas de produtos.
Quais são as principais propriedades dos materiais TPE?
Muitos fabricantes têm dificuldade em selecionar o tipo certo de TPE para as suas aplicações devido à confusão sobre as propriedades do material. Compreender as caraterísticas fundamentais dos materiais TPE é essencial para tomar decisões informadas sobre a seleção de materiais e métodos de processamento.
Os materiais TPE oferecem uma combinação única de propriedades que os tornam adequados para uma vasta gama de aplicações. Estas propriedades incluem flexibilidade, resiliência, resistência química e facilidade de processamento, tudo sem a necessidade de vulcanização ou reticulação.
 Demonstração das propriedades do material TPE mostrando flexibilidade e resiliência
Demonstração das propriedades do material TPE mostrando flexibilidade e resiliência
Propriedades fundamentais dos materiais TPE
Os materiais TPE são caracterizados por várias propriedades chave que os distinguem de outros polímeros:
Propriedades mecânicas
- Elasticidade: Os TPE apresentam uma elasticidade semelhante à da borracha, o que lhes permite esticar e voltar à sua forma original.
- Gama de dureza: Os TPE estão disponíveis numa vasta gama de níveis de dureza, normalmente de 5 Shore A (muito macio) a 70 Shore D (rígido).
- Resistência à tração: Dependendo do tipo, os TPE podem oferecer resistências à tração que variam entre 2-30 MPa.
- Resistência ao rasgamento: Muitas formulações de TPE oferecem uma boa resistência ao rasgamento e à abrasão.
Propriedades térmicas
- Ponto de fusão: Ao contrário das borrachas termoendurecíveis, os TPE têm um ponto de fusão distinto, normalmente entre 120-250°C, consoante o tipo.
- Temperatura de serviço: Os diferentes tipos de TPE oferecem diferentes gamas de temperaturas de serviço, de -50°C a +150°C.
- Estabilidade térmica: Alguns tipos de TPE mantêm as suas propriedades melhor do que outros quando expostos ao envelhecimento pelo calor.
Comparação com outros materiais
Compreender como os TPEs se comparam a outros materiais ajuda a tomar decisões informadas sobre a seleção de materiais:
| Imóveis | TPE | Borracha termoendurecível | Termoplásticos rígidos |
|---|
| Elasticidade | Elevado | Elevado | Baixa |
| Facilidade de processamento | Elevado | Baixo (requer vulcanização) | Elevado |
| Reciclabilidade | Sim | Não | Sim |
| Resistência química | Moderado a bom | Excelente | Varia |
| Custo | Moderado | Elevado (devido ao processamento) | Baixo a moderado |
| Coloribilidade | Excelente | Limitada | Excelente |
De acordo com investigação publicada na Polymer Engineering & ScienceOs materiais TPE oferecem vantagens de processamento significativas em relação à borracha convencional, mantendo muitas das caraterísticas de desempenho desejáveis, o que os torna cada vez mais populares em aplicações tradicionalmente dominadas pela borracha vulcanizada.
Quais são os diferentes tipos de materiais TPE?
O termo "TPE" engloba uma família de materiais com propriedades e aplicações variáveis. Esta diversidade cria frequentemente confusão aos fabricantes que tentam selecionar o tipo de TPE mais adequado às suas necessidades específicas.
O TPE não é um material único, mas sim uma categoria que inclui seis tipos principais, cada um com estruturas químicas, propriedades e caraterísticas de processamento únicas. Compreender estes diferentes tipos é crucial para selecionar o material certo para aplicações específicas.
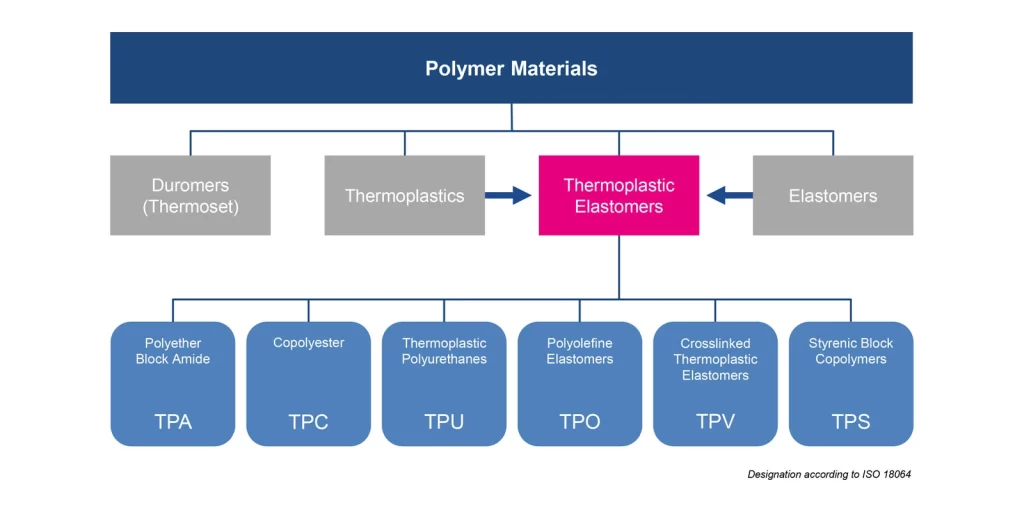 Diferentes tipos de materiais TPE com comparação visual
Diferentes tipos de materiais TPE com comparação visual
Tipos comuns de TPE:
Os TPE existem em várias formas, cada uma delas adequada a aplicações específicas:
- Poliolefinas termoplásticas (TPO): Misturas de polipropileno e borracha de etileno-propileno, apreciadas pela sua resistência às intempéries em peças para automóveis.
- Vulcanizados termoplásticos (TPV): Apresentam uma matriz termoplástica com partículas de borracha vulcanizada, ideal para aplicações resistentes ao calor.
- Poliuretanos termoplásticos (TPU): Oferecem resistência à abrasão e flexibilidade, sendo perfeitas para dispositivos médicos.
- Copolímeros de bloco estirénico (TPS): Incluem o SBS e o SEBS, utilizados em adesivos e bens de consumo.
| Tipo TPE | Propriedades principais | Utilizações comuns |
|---|
| TPO | Resistente às intempéries | Peças para automóveis |
| TPV | Resistente ao calor | Vedações industriais |
| TPU | Flexível, durável | Tubos médicos |
| TPS | Suave, adesivo | Bens de consumo |
Quais são as propriedades do TPE?
O que é que faz com que o TPE se destaque? As suas propriedades únicas fazem dele um favorito em todas as indústrias. Da flexibilidade à reciclabilidade, o TPE oferece um conjunto versátil de caraterísticas.
O TPE possui elasticidade, ascendência, suavidade, clareza, resistência às intempéries, resistência química e capacidade de processamento por fusão. Pode ser moldado, extrudido e reciclado facilmente.
Principais propriedades do TPE
As propriedades da TPE incluem:
- Elasticidade: Estica e retoma a sua forma, ideal para punhos e vedantes.
- Suavidade: Proporciona uma sensação de conforto para produtos médicos e de consumo.
- Clareza: Alguns TPEs são transparentes para aplicações estéticas.
- Resistência às intempéries: Resiste à luz UV e às intempéries para utilização no exterior.
- Resistência química: Resiste a óleos, gorduras e solventes.
- Processabilidade por fusão: Processos como os termoplásticos, aumentando a eficiência.
As tendências recentes destacam os TPE sustentáveis, como as opções de base biológica ou recicladas, que satisfazem as exigências ambientais.
As soluções de extrusão sustentável da Jinxin permitem que as fábricas produzam estes materiais ecológicos, alinhando-se com os objectivos globais de sustentabilidade. Estas propriedades fazem do TPE uma escolha de topo para os fabricantes que procuram desempenho e rentabilidade.
Quais são as aplicações dos materiais TPE?
Já reparou no TPE em produtos do quotidiano? A sua versatilidade brilha em inúmeras aplicações. Desde peças de automóvel a dispositivos médicos, o TPE melhora o desempenho e a sustentabilidade.
O TPE é utilizado em produtos automóveis, médicos, bens de consumo e industriais. A sua moldabilidade e reciclabilidade fazem dele uma escolha sustentável.
 O que é o material TPE? Desbloquear o seu potencial para o seu negócio 2
O que é o material TPE? Desbloquear o seu potencial para o seu negócio 2
Aplicações médicas e de cuidados de saúde
Os materiais TPE são cada vez mais utilizados em aplicações médicas devido à sua biocompatibilidade e flexibilidade:
- Tubos médicos: Os TPE são utilizados para tubos IV, cateteres e tubos de bombas peristálticas.
- Dispositivos médicos: Componentes como vedantes, juntas e pegas de toque suave para instrumentos médicos.
- Faixas elásticas: As nossas linhas de extrusão de bandas elásticas TPE produzem materiais utilizados em torniquetes, ligaduras Esmark e outras aplicações médicas.
De acordo com estudos de mercado, a espera-se que as aplicações médicas de TPE cresçam a uma taxa de crescimento anual de 9,0% até 2030, tornando-o um dos segmentos de crescimento mais rápido no mercado de TPE.
Produtos de consumo
Os materiais TPE melhoram muitos produtos de consumo quotidiano:
- Artigos para o lar: Utensílios de cozinha, escovas de dentes e componentes de electrodomésticos.
- Cuidados pessoais: Cabos de lâminas de barbear, pegas de escovas de cabelo e embalagens de cosméticos.
- Equipamento desportivo: Bandas de exercício, punhos para artigos desportivos e componentes para calçado.
Aplicações automóveis
A indústria automóvel é um dos principais consumidores de materiais TPE:
- Componentes interiores: Superfícies de toque suave, revestimentos do painel de instrumentos e botões de controlo.
- Aplicações exteriores: Vedantes contra intempéries, componentes do para-choques e guarda-lamas.
- Componentes sob o capô: Tubos de manuseamento de fluidos, isolamento de fios e vedantes.
 almofada para pés tpe
almofada para pés tpe
Construção civil
Os materiais TPE oferecem soluções para várias aplicações de construção:
- Sistemas de vedação: Vedações de janelas e portas, calafetagem e juntas de dilatação.
- Materiais para coberturas: Membranas de cobertura TPO e componentes de vedação.
- Componentes de canalização: Juntas, conectores flexíveis.
Como são processados os materiais TPE?
O processamento de materiais TPE apresenta desafios únicos em comparação com os plásticos ou borrachas convencionais. Muitos fabricantes lutam para conseguir uma qualidade e eficiência consistentes quando trabalham com estes materiais especializados.
Os materiais TPE podem ser processados utilizando métodos convencionais de processamento de termoplásticos, incluindo a extrusão, a moldagem por injeção, a moldagem por sopro e a termoformagem. Cada método requer configurações de equipamento e parâmetros de processamento específicos para obter resultados óptimos.
Processamento por extrusão de materiais TPE
A extrusão é um dos métodos mais comuns de processamento de materiais TPE:
Requisitos do equipamento de extrusão
- Conceção do parafuso: Os materiais TPE requerem normalmente parafusos com relações L/D de 24:1 a 30:1 e relações de compressão de 2,5:1 a 3,5:1.
- Controlo da temperatura: O controlo preciso da temperatura em várias zonas é essencial para o processamento adequado do TPE.
- Desenho do molde: As matrizes para extrusão de TPE devem ter percursos de fluxo optimizados para minimizar a queda de pressão e a degradação do material.
Parâmetros de processamento da extrusão
- Perfil de temperatura: O perfil de temperatura depende do tipo específico de TPE, mas geralmente varia entre 160-250°C.
- Velocidade do parafuso: Recomenda-se uma velocidade moderada do parafuso (normalmente 20-80 RPM) para evitar o aquecimento excessivo do corte.
- Arrefecimento: O arrefecimento controlado é fundamental para manter a estabilidade dimensional e a qualidade da superfície.
Na Jinxin Plastic Machinery, as nossas linhas de extrusão de elásticos TPE são especificamente concebidos para responder a estes requisitos de processamento, garantindo uma qualidade e eficiência consistentes.
Outros métodos de processamento de TPE
Moldagem por injeção
A moldagem por injeção é amplamente utilizada para produzir peças complexas de TPE:
- Considerações sobre o equipamento: Máquinas com capacidade de injeção, força de aperto e controlo de temperatura adequados.
- Parâmetros de processamento: Gamas de temperatura semelhantes às da extrusão, mas com atenção à velocidade de injeção, à pressão e ao tempo de arrefecimento.
- Aplicações: Componentes médicos, peças para produtos de consumo e componentes para interiores de automóveis.
De acordo com diretrizes de processamento dos principais fabricantes de TPEA secagem adequada, o controlo da temperatura e a seleção do equipamento são factores críticos para o sucesso do processamento de TPE. O nosso equipamento foi concebido com estas diretrizes em mente, garantindo condições de processamento ideais para várias formulações de TPE.
Como é que os materiais TPE se comparam à borracha e a outros elastómeros?
As decisões de seleção de materiais tornam-se frequentemente complicadas quando se comparam os materiais TPE com a borracha tradicional e outros elastómeros. Compreender as principais diferenças e vantagens é essencial para fazer escolhas informadas para aplicações específicas.
Os materiais TPE oferecem vantagens distintas sobre a borracha tradicional e outros elastómeros, particularmente em termos de eficiência de processamento e reciclabilidade. No entanto, também têm limitações que devem ser consideradas ao selecionar materiais para aplicações específicas.
TPE vs. Borracha termoendurecida
A diferença fundamental entre o TPE e a borracha termoendurecida reside na sua estrutura molecular e nas suas caraterísticas de processamento:
Vantagens de processamento do TPE
- Sem vulcanização: Os materiais TPE não necessitam de reticulação química (vulcanização), o que resulta em ciclos de processamento mais rápidos.
- Reciclabilidade: Os materiais TPE podem ser refundidos e reprocessados, ao contrário da borracha termoendurecida que não pode ser reciclada depois de vulcanizada.
- Eficiência energética: O processamento de TPE requer normalmente menos energia do que o processamento de borracha.
- Flexibilidade de conceção: Os materiais TPE podem ser processados através de vários métodos, oferecendo uma maior liberdade de conceção.
| Imóveis | TPE | Borracha termoendurecível |
|---|
| Temperatura máxima de serviço | Inferior (normalmente até 125°C) | Superior (até 200°C ou mais) |
| Resistência química | Bom para alguns produtos químicos, limitado para outros | Excelente para muitos produtos químicos |
| Conjunto de compressão | Geralmente mais elevado | Mais baixo (melhor retenção da forma) |
| Coloribilidade | Excelente | Limitada |
| Custo | Custo moderado do material, menor custo de processamento | Custo global mais elevado devido ao processamento
|
De acordo com investigação publicada no Journal of Applied Polymer ScienceEmbora os TPE possam não corresponder ao desempenho extremo de algumas borrachas especiais, oferecem um desempenho suficiente para muitas aplicações com vantagens de processamento significativas.
TPE vs. outros materiais termoplásticos
Os materiais TPE também oferecem vantagens em comparação com os termoplásticos rígidos:
- Flexibilidade: Os TPEs proporcionam uma flexibilidade semelhante à da borracha, não disponível nos termoplásticos rígidos.
- Toque suave: Os TPE oferecem propriedades tácteis agradáveis para produtos de consumo.
- Amortecimento de vibrações: Os TPEs proporcionam melhores propriedades de amortecimento de vibrações e de som.
- Resistência ao impacto: Muitas formulações de TPE oferecem uma excelente resistência ao impacto a baixas temperaturas.
O TPE é seguro?
Preocupado com a segurança em aplicações médicas ou alimentares? O TPE pode ser seguro quando formulado corretamente. É uma escolha fiável para utilizações sensíveis.
O TPE pode cumprir as normas de segurança da FDA e da UE para contacto com alimentos e aplicações médicas, sendo não tóxico e isento de aditivos nocivos.
Como selecionar o material TPE adequado para a sua aplicação?
A seleção do material representa um dos aspectos mais difíceis de trabalhar com materiais TPE. Com seis tipos principais e inúmeras formulações disponíveis, os fabricantes têm frequentemente dificuldade em identificar o material ideal para as suas necessidades específicas.
A seleção do material TPE adequado envolve a consideração de vários factores, incluindo requisitos de desempenho, condições de processamento, conformidade regulamentar e considerações de custo. Uma abordagem sistemática à seleção do material pode ajudar a garantir resultados óptimos.
O primeiro passo na seleção do material TPE é definir claramente os requisitos de desempenho:
- Propriedades mecânicas: Dureza, resistência à tração, alongamento e resistência ao rasgamento exigidos.
- Resistência ambiental: Exposição a UV, ozono, produtos químicos ou temperaturas extremas.
- Conformidade regulamentar: Especificações para contacto com alimentos, médicas ou automóveis.
- Requisitos estéticos: Cor, transparência, acabamento superficial e propriedades tácteis.
Considerações sobre o processamento
Os diferentes tipos de TPE têm caraterísticas de processamento variáveis que devem ser consideradas:
- Compatibilidade de equipamentos: Certifique-se de que o seu equipamento atual pode processar o tipo de TPE selecionado.
- Temperatura de processamento: Selecione materiais compatíveis com as capacidades de temperatura do seu equipamento.
- Requisitos de secagem: Alguns tipos de TPE requerem pré-secagem, enquanto outros não.
- Aplicações multi-materiais: Para a co-extrusão ou sobremoldagem, ter em conta a compatibilidade dos materiais.
Na Jinxin, ajudamos os clientes a avaliar as suas capacidades de processamento e recomendamos modificações de equipamento adequadas, se necessário, para materiais TPE específicos.
Matriz de seleção de materiais
Uma abordagem estruturada à seleção de EPT pode ser facilitada utilizando uma matriz de decisão:
| Requisito de candidatura | Tipos de TPE recomendados | Considerações |
|---|
| Alta flexibilidade, produtos de consumo | TPE-S (SEBS) | Boas propriedades tácteis, ampla gama de dureza, rentável |
| Durabilidade no exterior | TPE-O, TPE-V | Melhor resistência aos raios UV e ao ozono |
| Resistência a óleos/químicos | TPE-V, TPE-U, TPE-E | O TPE-V oferece a melhor resistência ao óleo para aplicações automóveis |
| Aplicações de alta temperatura | TPE-E, TPE-A | Temperaturas de serviço até 150°C |
| Aplicações médicas | TPE-S de grau médico, TPE-U | Biocompatibilidade, resistência à esterilização |
| Faixas elásticas | TPE-S, TPE-O | Boa recuperação elástica, processável na nossa Linhas de extrusão de elásticos TPE |
A nossa equipa técnica pode ajudar nos ensaios de processamento e fornecer orientações sobre as definições do equipamento para obter resultados óptimos com diferentes materiais TPE.
Conclusão: Aproveitamento dos materiais TPE para inovação e crescimento
Os materiais de TPE oferecem uma combinação única de propriedades que fazem a ponte entre os plásticos rígidos e a borracha vulcanizada. Ao compreender o que são os materiais TPE, os seus tipos, propriedades e requisitos de processamento, os fabricantes podem tirar partido destes materiais versáteis para desenvolver produtos inovadores e expandir as suas oportunidades de mercado.
Na Jinxin Plastic Machinery, estamos empenhados em ajudar os nossos clientes a ter sucesso com o processamento de TPE. O nosso equipamento especializado, conhecimentos técnicos e abordagem centrada no cliente fazem de nós o parceiro ideal para as suas necessidades de processamento de TPE. Contacte-nos hoje para saber como o podemos ajudar otimizar o seu material TPE processamento e expandir as capacidades dos seus produtos.
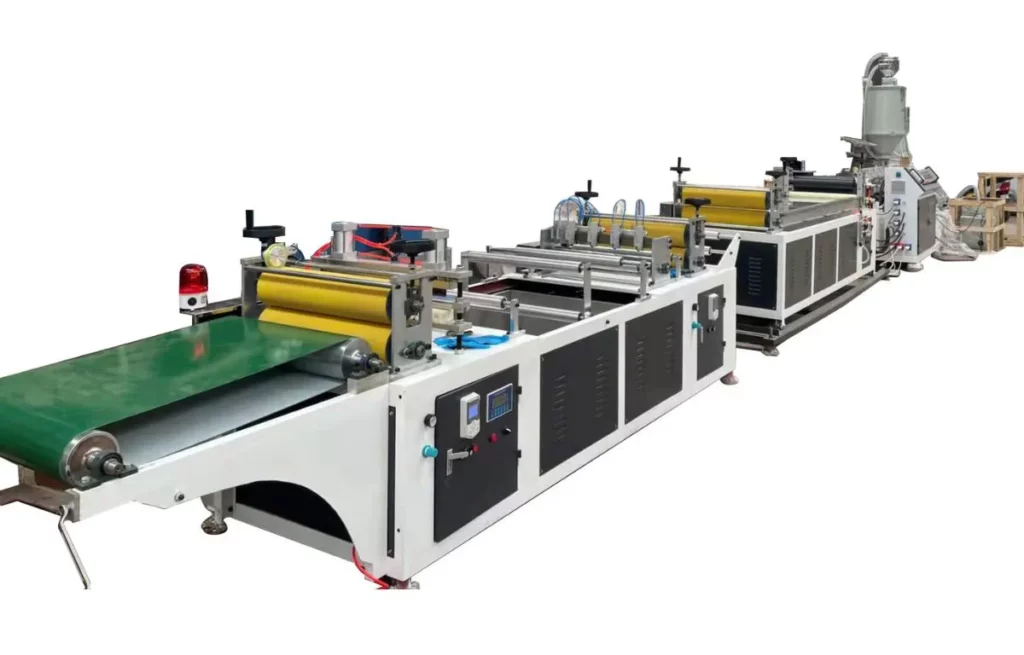 Linha de máquinas de extrusão de fita TPE
Linha de máquinas de extrusão de fita TPE